The benefits of tea have been widely known, began to help burn fat, a source of antioxidants, to relieve stress. Now, the tea will have a new benefits, which help humans to survive on Mars.
How can?
One type of tea are widely known in the world is Kombucha. The tea produced through fermentation with Komagataeibacter rhaeticus. The bacteria in Kombucha can produce a wide variety of cellulose which has now been widely used, began to cosmetics, skin substitutes, to snacks such as nata de coco.
 |
| Scientists have claimed bacteria in Kombucha tea (pictured) could help humans survive on Mars. (Picture from: http://adf.ly/1annwv) |
"What makes this find became a promising approach, we have shown that the production of cellulose can be controlled genetically, we can produce materials with different shapes, patterns and sizes," said Michael Florea, head of the research team.
 |
| Researchers in the UK have developed a new method of engineering bacterial cellulose to fit different purposes. The base component of the material is derived from bacteria typically found in fermented herbal tea known as kombucha. (Picture from: http://adf.ly/1anoUl) |
And the application of DNA-developed device can be varied.
Cellulose is produced by genetic engineering approach can be linked to a protein capable of binding contaminants. Furthermore, the cellulose can be used as a water purifier.
Cellulose can also be combined with chemical compounds that act as sensors. Thus, the cellulose can be used as a detector of toxic substances, the color will change to give a warning.
So how it could help humans to live on Mars?
When humans began to colonize the Mars, humans would need a lot of material resources for a variety of needs. The approach developed by Florea and his team offer an alternative for obtaining the resources.
Instead of bringing the material resources of the Earth are expensive, the earliest inhabitants of Mars can make the cellulose-based material with the help of bacteria in Kombucha. It is cheaper and easier. Now, Florea and his team are exploring the possibility of cooperation with the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). *** [EKA | FROM VARIOUS SOURCES | IRISH MIRROR | TECHTIMES]
Note: This blog can be accessed via your smart phone

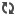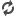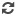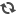 Logging you in...
Logging you in...