Scientists have uncovered the mystery behind Mars atmospheric conditions are cool and dry. In the past, the Red Planet atmosphere is believed to be very rich in carbon dioxide (CO2), but then absorbed by the rocks.
 |
| British researchers believe they have worked out how Mars lost its early carbon dioxide-rich atmosphere to become the cold and arid planet it is today. (Picture from: http://www.dailymail.co.uk/) |
This research is important for the survival on the Earth because it shows the first direct evidence of the occurrence of "carbonation" on Mars. The carbonation has impact on the CO2 disappearance from Martian atmosphere.
"Understanding the mechanisms of loss of carbon dioxide from the Martian atmosphere could be a clue to reduce the accumulation of greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere," said a scientists team from the Scottish Universities Environmental Research Centre, University of Glasgow, and the Natural History Museum in London.
Scientists say the accumulation of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere contribute significantly to global warming. Loss of carbon dioxide from the Martian atmosphere about 4 billion years ago, allegedly has triggered the cooling process on Mars.
In a paper that published in the Nature Communications journal, a scientists team describe the analysis of a Martian meteorite known as Lafayette. As quoted from Dailymail, Lafayette formed from molten rock about 1,300 billion year ago. And then a large collision which happen about 11 million years ago has been threw the rocks from Mars to the Earth's surface.
 |
| Researchers found evidence of carbonation by studying a meteorite known as Lafayette (pictured). The meteorite is thought to have landed on Earth roughly 3,000 years ago. (Picture from: http://www.dailymail.co.uk/) |
Recent research has focused on siderite. The carbon-rich minerals previously been found in Lafayette. Now a team of scientists found that the siderite formed through a carbonation process.
This process occurs when water and carbon dioxide from the Martian atmosphere reacting with rocks containing the olivine mineral. The reaction is then formed siderite crystals to replace olivine. This siderite which was capture of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it permanently in stone. *** [EKA | FROM VARIOUS SOURCES | DAILYMAIL | MAHARDIKA SATRIA HADI | KORAN TEMPO 4382]
Note: This blog can be accessed via your smart phone.
Note: This blog can be accessed via your smart phone.

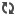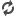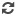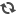 Logging you in...
Logging you in...